Introduction
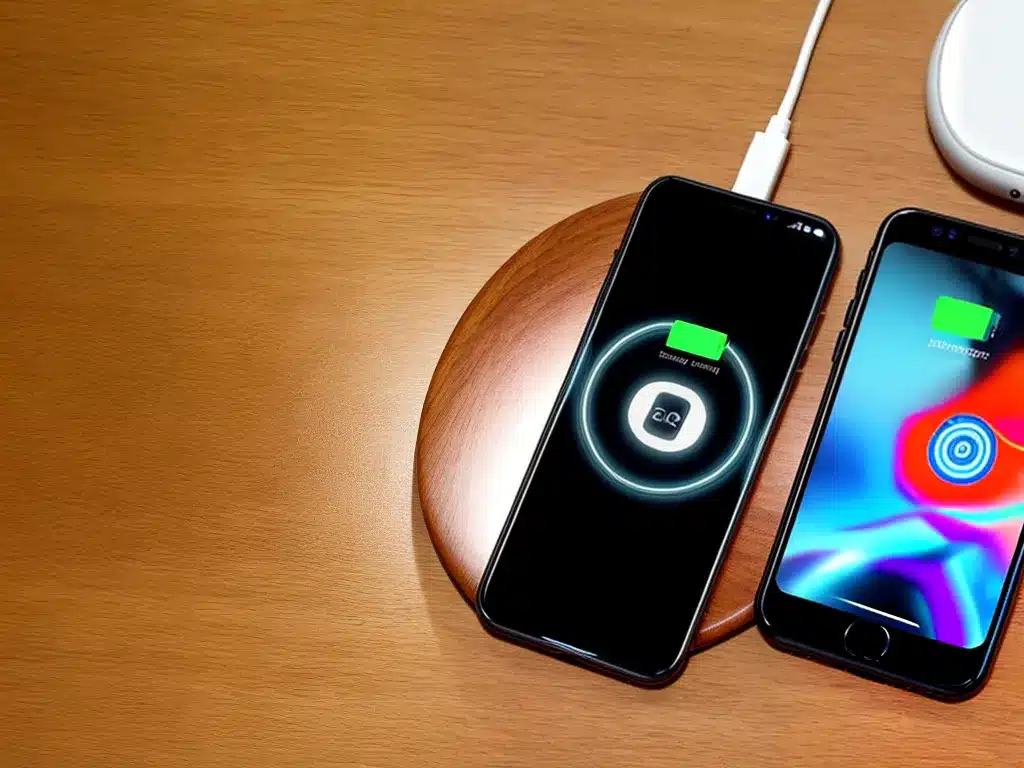
Wireless charging has become an increasingly popular technology over the past few years. It offers a convenient and cable-free way to charge our devices like smartphones, smartwatches, headphones, and more. In this article, I will provide an in-depth look at where wireless charging stands today and where it may be headed in the future. There are a few key questions I aim to answer:
- How does wireless charging work?
- What are the main wireless charging standards?
- What devices currently support wireless charging?
- What are the benefits and limitations?
- How fast is wireless charging compared to wired charging?
- What improvements can we expect in the future?
By the end, you should have a solid understanding of the current state of wireless charging technology and what the future may hold. Let’s get started!
How Does Wireless Charging Work?
Wireless charging, also known as inductive charging, uses an electromagnetic field to transfer energy between two objects – a charging pad or stand and a receiver built into the device. The charging pad contains a coil that generates an alternating electromagnetic field. When a device with a built-in receiving coil is placed on top, it converts the electromagnetic energy into electrical energy which charges the device’s battery.
The distance between the two coils is crucial – coils need to be close together, usually within a few millimeters, for wireless charging to work efficiently. The technology only requires charging pads and mobile devices to be in close proximity without being perfectly aligned.
Key Components
There are two main components that enable wireless charging:
-
Transmitter coil – This is built into the charging pad or stand. It generates an oscillating magnetic field when electrical current passes through it.
-
Receiver coil – This is built into the device being charged. When placed near the transmitter coil, the magnetic field induces an alternating electrical current in the receiver which is then rectified into usable DC power.
Main Wireless Charging Standards
There are a few industry standards that define wireless charging methods and ensure different devices can charge on compatible pads. Here are the main standards:
Qi
Qi (pronounced “chee”) was introduced in 2008 and is developed by the Wireless Power Consortium. It is the most widely adopted standard that works with over 3,000 devices from brands like Apple, Samsung, Sony, LG and more.
Qi chargers provide power up to 15W and operate at a frequency of 100-205 kHz. There are two types of Qi charging:
- Flat inductive charging – Devices lie flat and charge through electromagnetic induction.
- Resonance inductive charging – Allows more freedom in positioning with induction between transmitter and receiver coils.
AirFuel
AirFuel, formerly called PMA (Power Matters Alliance), is a standard created by the AirFuel Alliance. It supports power up to 15W and higher frequencies (277-357 kHz) compared to Qi.
While not as widely used as Qi, AirFuel is supported by brands like Samsung and Duracell. However, some Samsung devices support both Qi and AirFuel.
MagSafe
Apple introduced MagSafe wireless charging with the iPhone 12 series and MagSafe accessories. It uses magnets to align charging coils between the iPhone and MagSafe charger.
MagSafe supports faster 15W charging. It is currently only available for newer iPhones but may expand to other Apple devices.
What Devices Currently Support Wireless Charging?
Many major smartphone brands have started adopting wireless charging in their flagship devices. Here are some of the top smartphones and devices that support wireless charging:
- Recent iPhones (iPhone 8 and later)
- Recent Samsung Galaxy and Note phones
- Google Pixel phones (Pixel 3 and later)
- LG high-end phones
- Sony Xperia phones
- AirPods Pro and AirPods with Wireless Charging Case
- Apple Watch (Series 3 and later)
- Wireless headphones from brands like Beats, Jabra, JBL, etc.
- Electric toothbrushes like Oral-B Genius X
- Smartwatches from Apple, Samsung, Fossil, Mobvoi, etc.
- E-readers like the Kindle Oasis
- Wireless charging is also commonly built into cars, furniture, cafes, airports, and other public places.
So wireless charging is widely available across smartphones, earbuds, smartwatches, and other gadgets from major electronics companies. With the technology becoming more ubiquitous, compatibility across devices from different brands is improving too.
Benefits and Limitations of Wireless Charging
Let’s look at some of the key advantages and disadvantages of wireless charging:
Benefits
- Convenience – No cables or ports needed. Just place and charge.
- Portability – Small charging pads are easy to carry around.
- Universal – Can charge different devices on the same pad.
- Resistant to wear – No issues with broken charging ports.
- Water/dust-proofing – Easier for waterproof devices.
- Spatial freedom – Devices don’t need perfect alignment with the charger.
Limitations
- Slower charging – Wireless charging is slower than wired fast charging.
- Power efficiency – More energy is lost during wireless transmission.
- Single device – Most pads can charge just one device at a time.
- Positioning – Devices need to be aligned properly on the pad.
- Cost – Wireless chargers and receivers cost more than wired charging.
- Interference – Nearby metals can interfere and disrupt charging.
So in summary, wireless charging trades off some speed and power efficiency for increased convenience and usability. It’s a beneficial companion technology rather than a total replacement for wired charging.
Charging Speed Comparison
How fast is wireless charging compared to traditional wired charging methods? Let’s compare:
| Charging Method | Typical Charging Speed |
|-|-|
| Wired USB Charging | 5W |
| Fast Wired Charging (USB-C PD) | 18W+ |
| Qi Wireless Charging | 5-15W |
| Proprietary Wireless Charging | 15-30W |
- Qi and proprietary wireless charging is generally slower than fast wired charging standards like USB Power Delivery.
- But wireless charging is still faster than regular 5W wired charging.
- Some high-end wireless chargers using proprietary standards like MagSafe can reach faster speeds up to 30W.
- Charging speed also depends on the power rating of the wall adapter used. A higher wattage adapter provides faster charging.
So while wireless charging may not be the absolute fastest way to charge, it still provides decent charging speeds akin to regular wired charging. And the convenience it offers makes it preferable in many everyday situations.
The Future of Wireless Charging
Wireless charging technology is continuously evolving. Here are some exciting improvements we can expect to see in the next few years:
Faster Charging Speeds
New protocols will allow faster wireless charging – going up to 50-60W in the near future. This will help close the gap with speeds from wired fast charging.
Longer Range Charging
Companies are working on increasing the distance that wireless charging can work over, even at several feet away. This will give more placement flexibility.
Charging Multiple Devices
Wireless charging pads and stands that can charge multiple devices simultaneously will become more common. No need to take turns!
In-car Wireless Charging
More car makers will integrate wireless charging pads into automobile dashboards and interiors, allowing convenient charging on the go.
Over-the-air Charging
True wireless power transmission without contacts may someday charge our devices from a distance – still very much in R&D phase though.
Conclusion
Wireless charging adoption has grown tremendously over the past few years, with support from all major device manufacturers. Convenience is the biggest benefit although charging speeds have room for improvement. But continued innovation will likely close the gap with wired charging and add even more flexibility in the coming years. With wireless charging going mainstream, the days of plugging in may eventually become a thing of the past!