Introduction
Video game graphics have come a long way in the past few decades. From simple 2D sprites to fully interactive 3D environments, the increase in visual quality has been staggering. But there is still one holy grail that eludes designers and programmers: true photorealism. In this article, I will explore where we currently stand in the quest for perfect realism and what hurdles still need to be overcome.
Current State of Realism
Fidelity of Modern Games
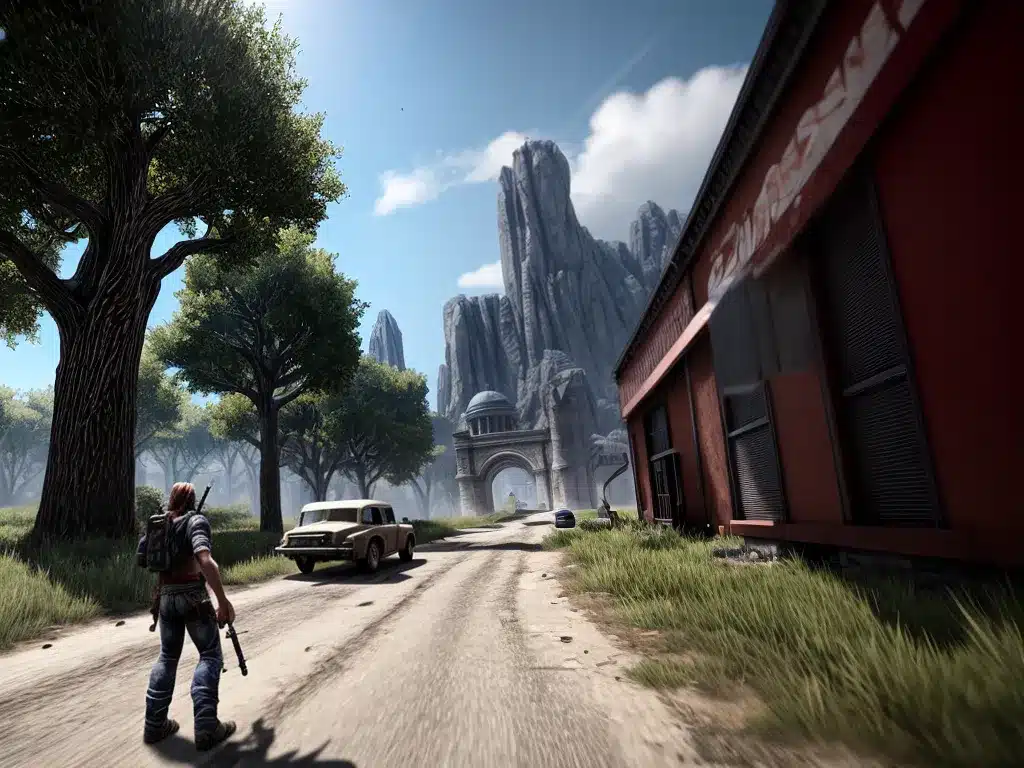
Modern games with high-end graphics can look extremely realistic already. Titles like Red Dead Redemption 2, The Last of Us Part II, and Microsoft Flight Simulator showcase some of the most impressive visuals ever seen in games. Intricately detailed character models, lifelike animations, and stunningly realistic environments create a heightened level of immersion. When coupled with advanced physics and particle effects, the visual experience borders on photorealistic fidelity.
Powerful Hardware Enabling Progress
The rapid advancement of consumer hardware plays a huge role in enabling more realistic graphics. Modern GPUs pack incredible processing power, allowing developers to include complex graphics features like ray tracing for realistic lighting. Higher display resolutions also increase fidelity – assets look sharper and cleaner at 4K than 1080p. More powerful hardware will pave the way for new graphics techniques.
New Rendering Techniques
Exciting new rendering techniques are also pushing realism forward. Ray tracing accurately simulates how light behaves in the real world. Photogrammetry uses photos of real objects to generate highly realistic 3D assets. Deep learning can enhance a wide range of graphical elements through AI and neural networks. As these technologies mature, graphics will become even more lifelike.
Remaining Challenges
The “Uncanny Valley”
While modern games look incredible, slight imperfections can make them seem strangely unrealistic. This phenomenon is known as the “uncanny valley” – as assets approach photorealism, tiny flaws become jarring. For example, an detailed character model with stiff facial animations may look obviously fake. Avoiding the uncanny valley remains an elusive goal.
Believable Animations and Interactions
Perfectly replicating how things move and interact in real life is incredibly difficult. Creating natural, believable animations for human characters is especially tricky. Similarly, making complex physics systems that handle materials and objects precisely like reality is an enormous challenge. This is key to making everything look seamlessly realistic.
Demanding Hardware Requirements
Cutting edge graphics technologies require incredibly powerful hardware. For example, ray tracing often cuts performance in half even on top-end GPUs. Building affordable consumer PCs that can handle advanced graphics well is difficult. Optimizing performance continues to be a priority.
Artistic Limitations
No matter how powerful the technology, there are artistic and human elements that are hard to replicate. Talented artists are needed to craft detailed 3D assets. Capturing the complexity of real world materials like skin is an art unto itself. There are intangible qualities of reality that technology alone cannot reproduce.
The Road Ahead
AI Assistance
Advances in AI will help automate and enhance aspects of development. AI can generate realistic animations and textures. It can also intelligently upscale assets while retaining detail integrity. This will empower artists and alleviate burdens.
Cloud Computing
Cloud computing can enable massive, detailed game worlds by offloading rendering and physics to remote servers. This additional power might make highly complex scenes achievable. Latency will remain a concern, but improvements in streaming could help.
Standardization of New Techniques
As new graphics features mature, they will become standardized across game engines and platforms. Ray tracing is already gaining traction in this manner. This will greatly increase adoption and let developers easily take advantage of them.
Gradual Iterative Improvement
Like most technology, progress towards photorealism in games will likely be gradual. But each iteration and hardware generation brings noticeable improvements. It may take many years before perfect realism is attained, but the incremental gains will be exciting.
Conclusion
Photorealism in games continues to inch closer, but challenges remain. Upcoming technologies like ray tracing, AI, cloud computing, and improved artistic techniques promise to close the gap considerably. While elusive, perfect realism is an inspiring goal, and the pursuit of it drives graphics innovation. Each small step forward brings us one pixel closer to capturing the true essence of reality. With dedication and imagination, game creators will someday fulfill the dream of games indistinguishable from life itself. But there is still much work to be done. The quest continues onward.