Understanding Graphics Card Failure
As someone who has been an avid PC gamer and enthusiast for many years, I’ve encountered my fair share of graphics card failures. It’s a frustrating and often perplexing issue that can leave you wondering what went wrong and how to fix it. In this comprehensive guide, I’ll delve into the common causes of graphics card failure, the warning signs to look out for, and the effective steps you can take to troubleshoot and resolve the problem.
Identifying the Signs of Graphics Card Failure
The first step in addressing a graphics card issue is to recognize the symptoms. What are the telltale signs that your graphics card is on its way out? I’ll outline the most common indicators, such as:
- Sudden system crashes or freezes during gameplay or graphics-intensive tasks
- Distorted or flickering display
- Artifacts or glitches on the screen
- Slow or unresponsive performance
- Overheating issues, with the graphics card running at abnormally high temperatures
By understanding these red flags, you can quickly diagnose the problem and take the necessary action to remedy the situation.
Exploring the Causes of Graphics Card Failure
Now that we’ve identified the symptoms, let’s delve into the underlying causes of graphics card failure. What are the factors that can lead to the demise of this critical component? I’ll cover a range of potential culprits, including:
-
Overheating: One of the leading causes of graphics card failure is overheating. When the card’s cooling system is inadequate or malfunctioning, the high temperatures can damage the delicate components, leading to performance issues and, ultimately, complete failure.
-
Electrical Surges and Power Fluctuations: Sudden power spikes or unstable electrical supply can overload and fry the graphics card’s circuitry, causing irreparable damage.
-
Physical Damage: Dropping or mishandling the graphics card during installation or transportation can result in physical damage to the components, leading to malfunctions.
-
Outdated or Incompatible Drivers: Failing to keep your graphics card drivers up-to-date or using the wrong drivers for your specific card can cause compatibility issues and instability, potentially leading to failure.
-
Excessive Wear and Tear: Like any other computer component, graphics cards have a finite lifespan. Over time, continuous use and stress can wear down the components, eventually causing the card to fail.
-
Manufacturing Defects: In some cases, graphics card failures can be attributed to inherent flaws or defects in the manufacturing process, which may not be immediately apparent.
Understanding these potential causes will help you better diagnose the root of the problem and take the appropriate steps to address it.
Troubleshooting Graphics Card Failure
Now that we’ve explored the common causes of graphics card failure, let’s delve into the troubleshooting process. What steps can you take to identify and resolve the issue? I’ll guide you through a comprehensive troubleshooting process, covering the following key steps:
-
Visual Inspection: Closely examine the graphics card for any physical damage, such as bent pins, cracked components, or signs of overheating.
-
Driver Updates: Ensure that you have the latest graphics card drivers installed. Outdated or incompatible drivers can often lead to performance issues and instability.
-
Power Supply Evaluation: Assess the capability and condition of your power supply unit (PSU). An inadequate or faulty PSU can cause instability and potentially damage the graphics card.
-
Cooling System Inspection: Check the graphics card’s cooling solution, including the heatsink, fans, and airflow. Ensure that the cooling system is functioning correctly and not impeded by dust or debris.
-
System Stress Testing: Run comprehensive system stress tests, such as benchmark software or demanding games, to identify any performance issues or stability problems.
-
Bios and Firmware Updates: Ensure that your system’s BIOS and any firmware updates for the graphics card are up-to-date, as outdated versions can contribute to stability problems.
-
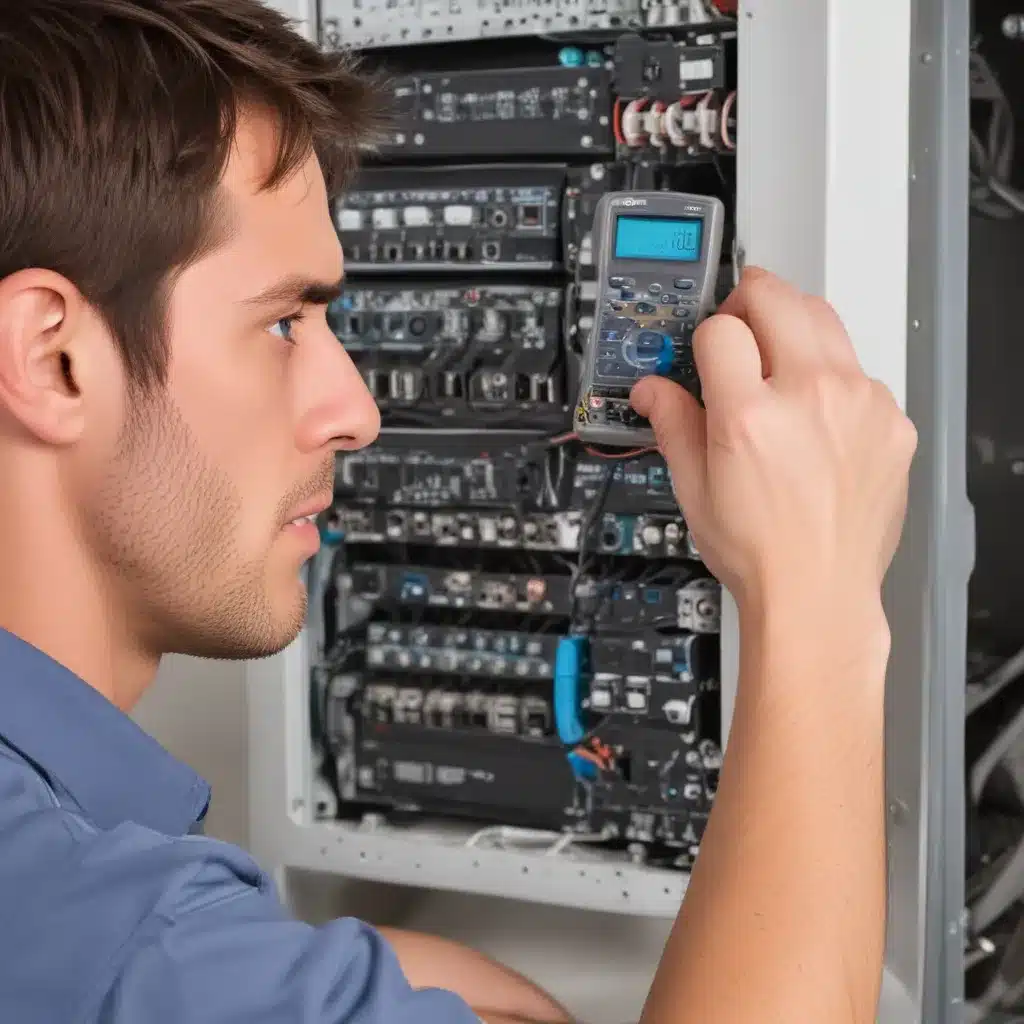
Hardware Diagnostics: Utilize diagnostic tools and software to analyze the health and performance of your graphics card, identifying any potential underlying issues.
-
GPU Replacement: If the troubleshooting process reveals a faulty or irreparable graphics card, you may need to consider replacing the component.
By following this step-by-step troubleshooting approach, you’ll be better equipped to identify the root cause of the graphics card failure and take the necessary actions to resolve the issue.
Preventive Measures for Graphics Card Longevity
Now that we’ve covered the common causes and troubleshooting steps for graphics card failure, let’s shift our focus to preventive measures. What can you do to prolong the lifespan of your graphics card and minimize the risk of future failures? I’ll share some essential tips and best practices:
Proper Cooling and Airflow Management
Maintaining an adequate cooling system is crucial for the longevity of your graphics card. Ensure that your PC case has sufficient airflow and that the graphics card’s cooling solution is functioning correctly. This may involve regularly cleaning the heatsink and fans, ensuring proper case ventilation, and potentially upgrading to a more robust cooling system if necessary.
Responsible Power Management
Managing the power supply to your graphics card is crucial. Ensure that your power supply unit (PSU) is capable of providing the necessary wattage and stability to your graphics card. Avoid subjecting the card to sudden power spikes or fluctuations, which can damage the sensitive components.
Keeping Drivers and Firmware Up-to-Date
Regularly updating your graphics card drivers and firmware can help prevent compatibility issues, stability problems, and potential hardware failures. Stay vigilant about driver updates, and always ensure that you’re using the latest versions recommended by the manufacturer.
Proper Installation and Handling
When installing or removing a graphics card, exercise caution and follow the manufacturer’s instructions precisely. Avoid excessive force or improper handling, as this can lead to physical damage to the card’s components.
Monitoring and Maintenance
Regularly monitoring the performance and temperature of your graphics card can help you identify potential issues before they escalate. Consider using system monitoring software to track the card’s temperature, utilization, and any warning signs of impending failure.
Timely Upgrades and Replacements
Like any other computer component, graphics cards have a finite lifespan. If your card is showing signs of aging or struggling to keep up with the demands of modern gaming and applications, it may be time to consider upgrading to a newer and more powerful model. Proactively replacing an aging graphics card can help you avoid the frustration of sudden failures and performance issues.
By implementing these preventive measures, you can significantly extend the lifespan of your graphics card and minimize the risk of untimely failures, ensuring a smooth and enjoyable computing experience.
Real-World Examples and Case Studies
To further illustrate the troubleshooting and prevention strategies, let’s explore some real-world examples and case studies of graphics card failure and how they were addressed.
Case Study 1: Overheating and Thermal Throttling
John, a passionate PC gamer, noticed his computer’s performance suddenly deteriorating during intense gaming sessions. Upon closer inspection, he discovered that his graphics card was running at abnormally high temperatures, causing it to throttle its performance to prevent overheating.
To address the issue, John first cleaned the graphics card’s cooling system, removing any accumulated dust and debris. He also ensured that the case’s airflow was optimized, with adequate intake and exhaust fans. Additionally, he monitored the graphics card’s temperature using specialized software and adjusted the system’s fan curves to maintain a lower operating temperature.
By implementing these measures, John was able to successfully mitigate the overheating problem and restore his graphics card’s performance to its expected levels, preventing any further damage.
Case Study 2: Power Supply Failure and Compatibility Issues
Sarah, a video editing professional, experienced sudden system crashes and display artifacts while working on a complex project. After troubleshooting, she determined that the issue was related to her graphics card.
Further investigation revealed that her power supply unit (PSU) was underpowered and unable to provide the necessary stability and wattage required by her graphics card. Sarah promptly upgraded to a higher-quality, more powerful PSU that was compatible with her system’s specifications.
The switch to a suitable power supply resolved the system crashes and display issues, allowing Sarah to continue her work without interruption.
Case Study 3: Driver Incompatibility and Firmware Updates
Alex, a PC enthusiast, encountered frequent game crashes and stuttering performance on his newly built gaming rig. After running various diagnostics, he discovered that the issue was related to the graphics card drivers.
Alex proceeded to thoroughly research the latest driver updates released by the graphics card manufacturer. He then carefully uninstalled the existing drivers and installed the recommended updates, ensuring a clean and compatible installation.
Additionally, Alex checked for any available firmware updates for his graphics card and applied them as directed by the manufacturer. This comprehensive approach to driver and firmware management resolved the performance issues and stabilized his system, allowing him to enjoy his games without interruption.
These real-world examples illustrate the importance of understanding the underlying causes of graphics card failure, implementing effective troubleshooting strategies, and taking preventive measures to ensure the longevity and reliable performance of this critical component.
Conclusion
In conclusion, dealing with graphics card failure can be a frustrating and complex issue, but by understanding the common causes, recognizing the warning signs, and following a comprehensive troubleshooting process, you can effectively address and resolve the problem.
Throughout this guide, I’ve covered the key aspects of graphics card failure, from identifying the symptoms to exploring the underlying causes and implementing preventive measures. By applying the strategies and best practices outlined here, you’ll be better equipped to extend the lifespan of your graphics card and maintain a stable and high-performing computing experience.
Remember, regular maintenance, proactive upgrades, and a vigilant approach to power management and cooling are all essential elements in safeguarding the health and longevity of your graphics card. By embracing these principles, you can confidently tackle any graphics card-related challenges that may arise, ensuring your system remains a reliable and powerful companion for all your computing needs.