Repairing Physical Damage to Laptop Hinges and Chassis
As an experienced IT professional, I’ve seen my fair share of laptop repair challenges. One common issue that often arises is physical damage to the laptop’s hinges and chassis. Whether it’s from accidental drops, wear and tear, or improper handling, these hardware components can take a beating over time. In this comprehensive guide, I’ll walk you through the steps to assess, diagnose, and repair physical damage to your laptop’s hinges and chassis.
Laptop Hardware Components
To understand the repair process, let’s first dive into the key components involved.
Laptop Chassis
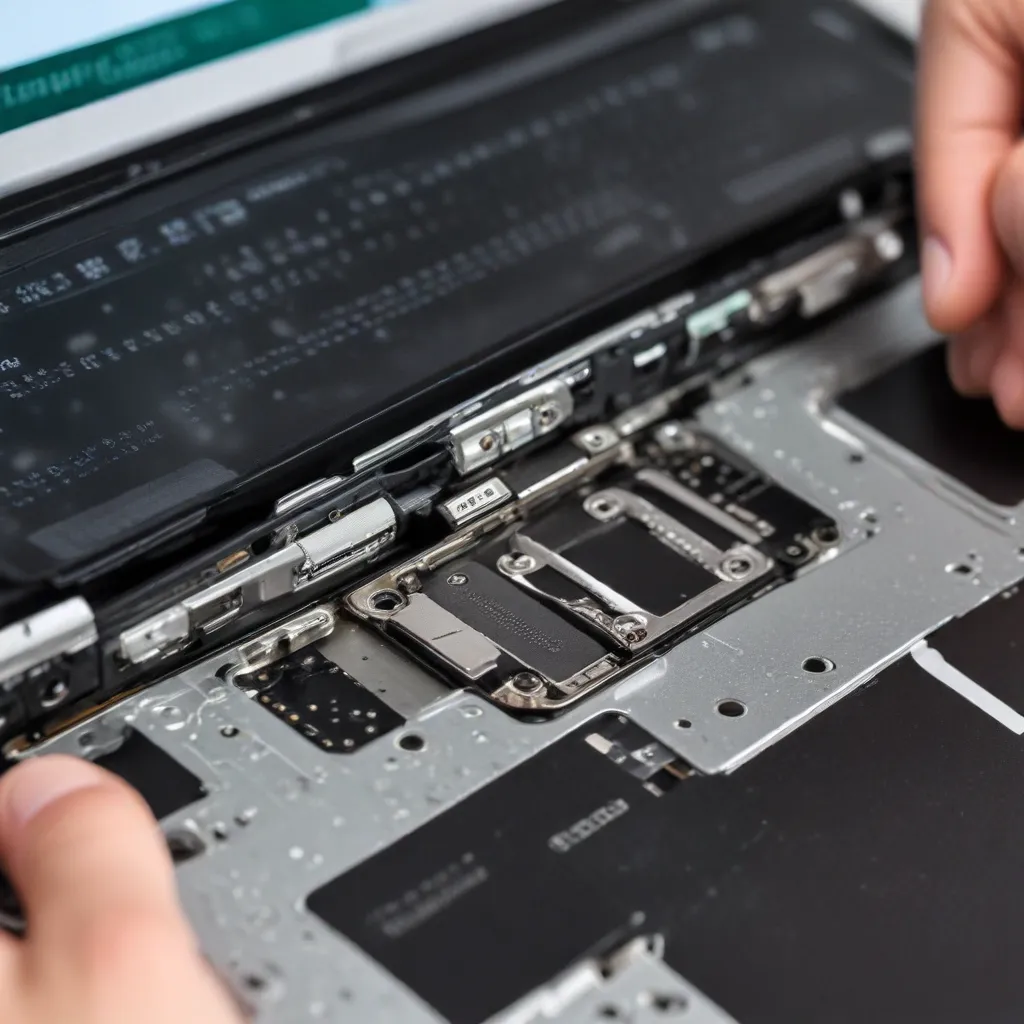
The laptop chassis, also known as the casing or body, is the outer shell that encases the internal hardware. It’s typically made of materials like plastic, metal, or a combination of both. The chassis protects the sensitive components inside and provides the overall structural integrity of the device.
Laptop Hinges
The hinges are the pivotal points that connect the display to the main body of the laptop. They allow the screen to smoothly open and close, enabling the laptop’s versatile functionality. Hinges are often one of the most vulnerable parts of a laptop, as they bear the brunt of daily use and movement.
Display Assembly
The display assembly, which includes the screen, bezel, and surrounding frame, is another critical component that can be affected by physical damage. Issues with the display assembly can range from cracked screens to peeling bezels.
Laptop Physical Damage
Now that we’ve covered the key hardware components, let’s explore the types of physical damage that can occur and the common causes behind them.
Types of Physical Damage
Physical damage to laptops can manifest in various ways, including:
- Chassis cracks or separation: Cracks or gaps appearing in the laptop’s outer casing, often near the corners or edges.
- Hinge issues: Hinges that feel loose, stiff, or make grinding noises when opening and closing the display.
- Display assembly problems: Cracked, scratched, or peeling screens; damaged or detached bezels.
Causes of Physical Damage
The primary culprits behind physical damage to laptops are:
- Accidental drops or impacts: Laptops can take a beating when they’re dropped, bumped, or knocked off surfaces.
- Excessive force or pressure: Applying too much force when opening, closing, or handling the laptop can strain the hinges and chassis.
- Wear and tear over time: Prolonged use and repeated opening/closing of the display can gradually wear down the hinges and chassis.
- Improper storage or transportation: Cramming a laptop into a tight space or carelessly tossing it into a bag can lead to physical damage.
Assessing the Damage
When dealing with physical damage, it’s crucial to carefully assess the extent of the problem before attempting any repairs. Look for visible cracks, gaps, or misalignment in the chassis, examine the hinges for any signs of wear or looseness, and inspect the display assembly for any cracks, scratches, or detached components.
Laptop Repair Techniques
Once you’ve identified the specific issue, it’s time to explore the repair options. Keep in mind that the complexity of the repair will depend on the type and severity of the damage.
Disassembly Procedures
Repairing physical damage often requires partial or complete disassembly of the laptop. This process involves carefully removing the bottom cover, accessing the internal components, and potentially detaching the display assembly. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions or seek guidance from online repair tutorials to ensure a safe and successful disassembly.
Replacement Parts
Depending on the extent of the damage, you may need to replace specific components, such as the hinges, chassis, or display assembly. Ensure that you source genuine, compatible replacement parts from reliable suppliers or the laptop manufacturer to maintain the device’s integrity and performance.
Reassembly and Testing
After completing the necessary repairs, meticulously reassemble the laptop, ensuring that all components are properly aligned and secured. Conduct thorough testing to verify that the repaired areas are functioning correctly and that the laptop is operating without any issues.
Preventive Maintenance Strategies
To minimize the risk of physical damage to your laptop, consider the following preventive maintenance strategies:
Proper Handling Techniques
Be mindful of how you handle your laptop. Avoid carrying it by the display, applying excessive force when opening or closing the lid, and placing heavy objects on top of the device.
Protective Accessories
Invest in a high-quality laptop sleeve, case, or backpack to provide an extra layer of protection during transportation and storage.
Regular Inspections
Routinely inspect your laptop’s hinges, chassis, and display assembly for any signs of wear or damage. Address issues promptly to prevent them from escalating.
Laptop Troubleshooting
While physical damage is a common problem, it’s important to rule out other potential hardware or software issues that could be contributing to the problem.
Identifying Hardware Issues
Carefully examine the laptop for any additional problems, such as loose connections, faulty components, or signs of overheating. These underlying issues may exacerbate the physical damage or prevent successful repairs.
Isolating the Problem
Perform targeted troubleshooting to isolate the root cause of the problem. This may involve testing individual components, running diagnostic tools, or seeking professional assistance.
Seeking Professional Help
For complex or severe physical damage, or if you’re unsure about the repair process, it’s best to consult a professional laptop repair service. They have the expertise and specialized tools to handle intricate repairs effectively.
Laptop Warranty and Support
Before attempting any DIY repairs, be sure to check the warranty coverage and support options available for your laptop.
Manufacturer Warranties
Many laptop manufacturers offer warranty coverage for hardware issues, including physical damage. Consult the warranty terms to see if your specific problem is eligible for repair or replacement.
Extended Warranty Options
Consider investing in an extended warranty or accidental damage protection plan to safeguard your laptop against future physical mishaps.
Third-Party Repair Services
If your laptop is no longer under warranty, or the damage is not covered, explore reputable third-party repair services that specialize in laptop hardware repairs.
By understanding the various components, common damage types, repair techniques, and preventive maintenance strategies, you’ll be better equipped to tackle physical damage to your laptop’s hinges and chassis. Remember, when in doubt, it’s always best to seek professional assistance to ensure the longevity and performance of your valued device.












