In today’s digital world, where we rely heavily on a plethora of USB-powered devices, it’s crucial to understand the importance of maintaining and troubleshooting USB ports and connectors on our laptops and desktops. Whether you’re a tech-savvy individual or an IT professional, mastering the art of diagnosing and repairing USB-related issues can save you time, money, and the frustration of dealing with unresponsive or malfunctioning devices.
USB (Universal Serial Bus) Technology
The USB protocol has evolved significantly over the years, with each iteration offering improved data transfer speeds, power delivery capabilities, and connector designs. Understanding the various USB versions and connector types can be helpful when troubleshooting USB-related problems.
USB Versions and Specifications
The most commonly used USB versions are USB 2.0, USB 3.0, USB 3.1, and USB-C. Each version offers different data transfer speeds, power delivery capabilities, and physical connector designs. For example, USB 2.0 has a maximum data transfer rate of 480 Mbps, while USB 3.0 and USB 3.1 can achieve up to 5 Gbps and 10 Gbps, respectively.
USB Connector Types
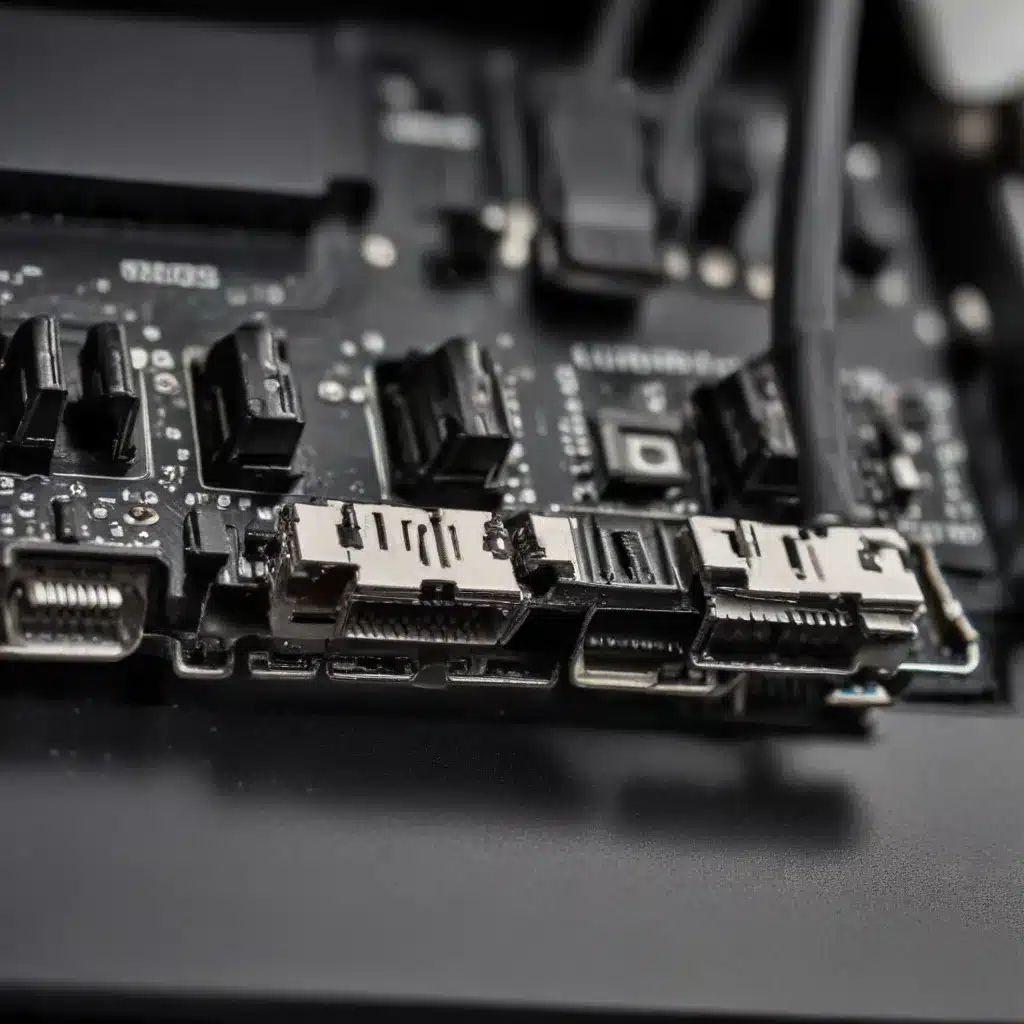
The most prevalent USB connector types are USB Type-A, USB Type-B, and USB-C. Type-A connectors are the familiar rectangular shape found on most computers, while Type-B connectors are commonly used on peripherals like printers and external hard drives. The newer USB-C connector is reversible and designed to be more versatile, supporting higher data transfer speeds and power delivery.
Laptop and Desktop USB Ports
Laptops and desktops typically have a combination of integrated and expansion USB ports. Integrated USB ports are built directly into the motherboard or chassis, while expansion USB ports are added via PCI or PCIe expansion cards.
Integrated USB Ports
Integrated USB ports are the most common type found on laptops and desktops. These ports are directly connected to the computer’s chipset and are responsible for communicating with USB devices.
Expansion USB Ports
In some cases, users may need additional USB ports beyond those provided by the integrated ports. Expansion USB ports can be added using PCI or PCIe expansion cards, which are installed directly into the computer’s expansion slots.
Diagnosing USB Port and Connector Issues
USB port and connector issues can arise due to both hardware-related and software-related problems. Understanding the root cause of the issue is crucial for effective troubleshooting and repair.
Hardware-related Problems
Physical Damage: Over time, USB ports and connectors can become worn, bent, or physically damaged, leading to connectivity issues. This can be caused by excessive use, improper insertion of devices, or accidental impacts.
Electrical Faults: USB ports and connectors are susceptible to electrical faults, such as short circuits or power surges, which can damage the internal components and cause malfunctions.
Software-related Problems
Driver Conflicts: Outdated, incompatible, or corrupt USB device drivers can cause USB ports to become unresponsive or unreliable. This is especially common when installing new hardware or upgrading the operating system.
Power Management Settings: Improper power management settings can also contribute to USB port issues, as the computer may not be providing enough power to connected devices.
Troubleshooting USB Port and Connector Failures
When faced with USB port or connector issues, it’s essential to follow a systematic troubleshooting approach to identify and resolve the problem.
Systematic Troubleshooting Approach
Visual Inspection: Begin by visually inspecting the USB ports and connectors for any signs of physical damage, such as bent pins, dust accumulation, or discoloration.
Connectivity Testing: Test the USB ports and connectors by plugging in known-working devices to ensure they are functioning correctly. If a device is not recognized or doesn’t work, the issue may be with the port or connector.
Device Manager Checks: Use the Windows Device Manager to check the status of USB devices and their associated drivers. Look for any device conflicts, errors, or outdated drivers that may be causing the problem.
Repair and Replacement Strategies
Cleaning and Maintenance: Use a can of compressed air to gently clean the USB ports and connectors, removing any dust or debris that may be interfering with the connection.
Component Replacement: If the USB ports or connectors are physically damaged, you may need to replace the entire component. This could involve replacing the motherboard, USB expansion card, or the laptop’s USB ports.
USB Port and Connector Optimization
While troubleshooting and repairing USB-related issues is essential, it’s also important to consider ways to optimize the performance and security of your USB ports and connectors.
Performance Considerations
USB Data Transfer Speeds: Ensure that your USB ports are capable of supporting the desired data transfer speeds for your devices. Upgrading to newer USB versions, such as USB 3.0 or USB 3.1, can significantly improve data transfer performance.
Power Delivery Capabilities: Some USB ports are designed to provide higher power delivery, which is essential for charging devices or powering high-draw peripherals. Make sure your USB ports can meet the power requirements of your connected devices.
Security and Safety Measures
USB Port Disabling: For added security, you may want to consider disabling unused USB ports to prevent unauthorized access or the introduction of malware through USB devices.
Antivirus and Malware Protection: Ensure that your computer’s antivirus and malware protection software is up-to-date and actively monitoring USB devices for any potential threats.
By following the steps outlined in this comprehensive guide, you’ll be well-equipped to diagnose and repair any issues related to USB ports and connectors on your laptops and desktops. Remember, proactive maintenance and a systematic troubleshooting approach can go a long way in keeping your devices running smoothly and efficiently.
If you’re still experiencing persistent USB-related problems after trying the recommended solutions, it’s always a good idea to seek the assistance of a professional IT technician or service provider. They can provide expert-level guidance and access to specialized tools and resources to resolve even the most complex USB issues.
Stay connected, stay secure, and keep your devices running at their best with this guide to diagnosing and repairing faulty USB ports and connectors.












