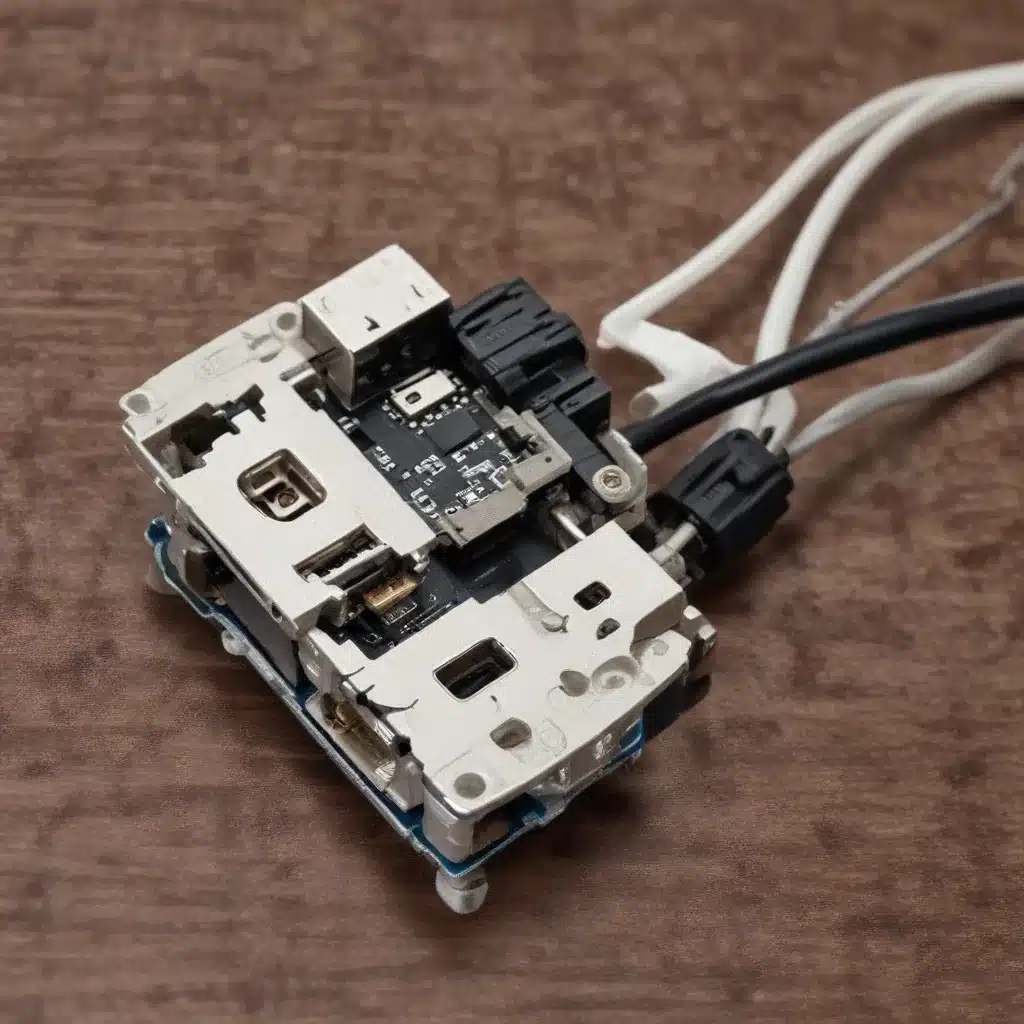
Repairing Damaged USB Ports and Cables – A DIY Guide
The USB (Universal Serial Bus) protocol has become an essential part of our digital lives, enabling seamless connectivity between a wide range of devices, from computers and smartphones to peripherals and IoT gadgets. However, like any technology, USB ports and cables can sometimes fall victim to wear and tear, leading to connectivity issues or even complete failure. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the common problems associated with USB ports and cables, and provide you with the knowledge and skills to tackle these challenges through DIY repairs.
USB Ports: The Backbone of Connectivity
Types of USB Ports
USB ports come in various shapes and sizes, each with its own unique specifications and capabilities. The most common USB port types include:
- USB Type-A: The original and most widely used USB port, found on desktops, laptops, and many other devices.
- USB Type-B: Commonly used for printers, scanners, and external hard drives.
- USB Type-C: The latest USB standard, designed to be reversible and support faster data transfer and power delivery.
- USB Mini and Micro: Smaller versions of the USB ports, primarily found on smartphones, digital cameras, and other portable devices.
USB Port Damage
USB ports can suffer from a variety of issues, including:
- Physical Damage: Bent, broken, or loose pins within the port can disrupt the connection.
- Corrosion: Exposure to moisture, dust, or chemicals can lead to corrosion, causing connection problems.
- Overuse: Frequent plugging and unplugging of cables can wear down the port over time.
- Static Electricity: Electrostatic discharge can damage the sensitive electronic components within the port.
Understanding the potential problems with USB ports is the first step in addressing and repairing them.
USB Cables: The Lifeline of Data Transfer
USB Cable Specifications
USB cables come in different versions, each with its own capabilities and specifications:
- USB 2.0: Supports data transfer speeds up to 480 Mbps.
- USB 3.0/3.1: Offers significantly faster data transfer speeds, up to 5 Gbps (USB 3.0) or 10 Gbps (USB 3.1).
- USB-C: The latest USB standard, capable of delivering up to 100W of power and supporting data transfer speeds up to 20 Gbps.
USB Cable Failure
USB cables can also experience various problems, such as:
- Frayed or Damaged Wires: Repeated bending, excessive tension, or physical damage can lead to broken or exposed wires.
- Loose Connections: Wear and tear on the cable ends can result in loose or unreliable connections.
- Compatibility Issues: Using the wrong type of USB cable for a specific device can cause compatibility problems.
Recognizing the different USB cable specifications and potential failure points is crucial for effective troubleshooting and repair.
Diagnosing USB Issues
Common USB Problems
When dealing with USB-related issues, you may encounter a range of problems, including:
- No Power Delivery: The device is not receiving the necessary power through the USB connection.
- Data Transfer Failures: Files or data cannot be successfully transferred between devices.
- Intermittent Connectivity: The USB connection keeps dropping or experiencing frequent disconnections.
- Device Not Recognized: The connected device is not being detected by the host system.
Identifying the specific problem is the first step in determining the appropriate course of action for resolving the issue.
USB Diagnostics
Hardware Diagnostics
To diagnose hardware-related USB problems, you can perform the following steps:
- Visual Inspection: Examine the USB port and cable for any physical damage, such as bent or broken pins, frayed wires, or corrosion.
- Connectivity Test: Try using the USB device with a different port or cable to isolate the problem.
- Power Verification: Ensure that the USB port is providing the necessary power to the connected device.
Software Diagnostics
In addition to hardware diagnostics, you can also utilize software tools to troubleshoot USB issues:
- Device Manager: Check the Device Manager on your Windows or macOS system for any USB-related errors or device conflicts.
- USB Troubleshooter: Use the built-in USB troubleshooter in Windows or the USB Prober tool on macOS to identify and resolve USB-related problems.
- USB Diagnostics Tools: Leverage specialized USB diagnostic software, such as USBDeview or USB Viewer, to analyze the health and status of your USB devices and connections.
By combining hardware and software diagnostics, you can effectively pinpoint the root cause of your USB problems and determine the appropriate course of action for repair.
USB Port Repair
Physical Repair
Replacing USB Ports
If the USB port on your device is physically damaged, the best solution is to replace the port. This process typically involves the following steps:
- Disassemble the Device: Carefully open the device to access the internal components and the USB port.
- Disconnect the Existing Port: Carefully remove the damaged USB port, taking note of the wiring and connections.
- Install the Replacement Port: Solder the new USB port in place, ensuring proper alignment and secure connections.
- Reassemble the Device: Put the device back together, taking care to avoid any damage to the internal components.
This process can be delicate and may require advanced soldering skills, so it’s recommended to seek the assistance of a professional if you’re not comfortable with electronics repair.
Soldering Techniques
For DIY USB port repair, you may need to learn basic soldering techniques. This involves:
- Preparing the Surfaces: Thoroughly clean the surfaces to be soldered, removing any dirt, oxidation, or residue.
- Applying Solder: Use a soldering iron and lead-based solder to create a secure connection between the port and the device’s circuit board.
- Avoiding Overheating: Be mindful of the temperature and duration of the soldering process to prevent damage to the delicate components.
- Inspecting the Connections: Carefully inspect the soldered joints to ensure a strong, reliable connection.
Practicing your soldering skills on non-essential components before attempting a USB port repair can help build your confidence and ensure a successful outcome.
Software Solutions
USB Driver Updates
Outdated or incompatible USB drivers can sometimes cause connectivity issues. Ensure that you have the latest USB drivers installed for your operating system and device-specific components.
- Check for Driver Updates: Visit the manufacturer’s website or use the built-in Windows Update or macOS Software Update to find and install the latest USB drivers.
- Manually Update Drivers: If the automatic update process is not successful, you can manually download and install the appropriate USB driver package.
System Configuration
In some cases, adjusting the system configuration can help resolve USB-related problems:
- Power Management Settings: Ensure that the USB ports are not being disabled or entering a power-saving mode.
- USB Selective Suspend: Disable the USB Selective Suspend setting, which can sometimes cause connectivity issues.
- USB Troubleshooting: Use the built-in USB troubleshooting tools in Windows or macOS to diagnose and resolve any system-level USB problems.
By addressing both the physical and software aspects of USB port repair, you can effectively restore the functionality of your devices and ensure reliable USB connectivity.
DIY USB Cable Repair
Cable Inspection
Before attempting to repair a damaged USB cable, it’s important to thoroughly inspect it to identify the specific issue:
- Visual Inspection: Carefully examine the cable for any visible signs of damage, such as frayed wires, cracks, or breaks in the insulation.
- Connectivity Test: Use a multimeter or continuity tester to check the integrity of the cable’s connections, ensuring that all pins are properly conducting electricity.
- Power Delivery Test: Verify that the cable is capable of delivering the necessary power to the connected device.
By accurately diagnosing the problem, you can determine the best course of action for repairing or replacing the USB cable.
Cable Replacement
If the USB cable is beyond repair, replacing it may be the most practical solution. Here’s how you can approach the process:
- Sourcing Replacement Cables: Identify the specific type of USB cable you need, taking into account the device’s requirements and the desired data transfer and power delivery capabilities.
- Cable Replacement Procedure: Carefully disconnect the old cable and connect the new one, ensuring that the pins and connections are properly aligned.
When replacing a USB cable, it’s essential to use a high-quality, compatible replacement to ensure optimal performance and reliability.
By following the steps outlined in this comprehensive guide, you can effectively diagnose and repair damaged USB ports and cables, restoring the connectivity and functionality of your devices. Remember, if you’re not comfortable with electronics repair, it’s always best to seek the assistance of a qualified technician. Happy troubleshooting and happy tinkering!












